- 回首頁
- 機械工業雜誌
- 歷史雜誌
摘要:經統計目前國內水五金相關廠商約300家,大多以出口為主,供應全球50%以上水龍頭,而全球科技研究與顧問公司Technavio在最新的研究預測報告中指出,全球水龍頭市場在2018年至2022年期間其市場規模將增加65億美元,且需求量有逐年上升的趨勢[1]。水五金工件具複雜外型、多維度曲面之特性,目前研磨製程需靠師傅邊磨邊檢以確保產品品質,恐發生品質不均、經驗難以傳承與自動化困難之問題。為因應曲面鑄件表面之研磨品質回饋需求,本文將介紹以機器視覺與相位移輪廓法(Phase Measuring Profilometry, PMP) 結合方式,開發3D表面研磨品質回饋技術,以達成非接觸式之快速評估表面研磨情形,解決現有複雜形狀工件研磨製程之檢測需求,提升傳統製造業之附加價值。
Abstract:According to the statistics, there are around 300 faucet makers in Taiwan, while most of them are export-oriented and are account for 50% of the global faucet market share. TechNavio, a global leading technology research and advisory company indicated in their latest market research report that the overall sales of global faucet industry will increase by 65 billion US dollars from 2018 to 2022, which indicates the trend of growing demands in this industry. Faucets have the features of complicated contours and multi-dimensional shapes. Commonly, manual inspection in grinding process to ensure the surface quality of faucets is employed. This pose problems for the inconsistency of the grinding quality, difficulty in the succession of labors’ experience and barriers to the implementation of automation in the factory. Therefore, in order to meet the requirements of knowing the surface condition during the grinding process automatically, a method which utilizes machine vision with phase measuring profilometry (PMP) technique to obtain the 3D surface feature grading as visual feedback for robot cyber physic systems is proposed in this paper. Experimental results show that a non-contact curved contour inspection method has been validated to quickly to distinguish surface grinding level as the quality feedback, allowing manufacturers to meet the needs of complex tool surface inspection during grinding operation to add values for traditional manufacturing industries.
關鍵詞:機器視覺、相位移輪廓法、網絡實體系統
Keywords:Machine vision, Phase measuring profilometry, Cyber-physical system
前言
網絡實體系統(Cyber-Physical System, CPS)為「工業4.0」的關鍵技術[2-3],是一種配備嵌入式感測器、運算處理器與致動器的系統,實際運作時能夠將數位虛擬(Cyber)與實體裝置(Physical)間的資料進行連結。近年來,隨著工廠自動化的需求,如何使用自動化技術來取代傳統人工重複性高、低附加價值及高可靠度之工作,也變成重要之課題。
本文主要目的是想要解決現有曲面鑄件表面研磨製程之檢測需求,傳統鑄件表面研磨製程只有部分自動化,主要原因是水龍頭表面是3D曲面並非2D平面,研磨時會需要依據鑄件表面形狀來調整機器手臂的姿態,而在機器手臂研磨後,往往還是需要使用人工的方式進行修補,圖1a中紅色框選區域是傳統自動化的研磨結果,可以發現在複雜曲面的位置可能會存在著未研磨到之現象,圖1b則為經由人工輔助研磨後之結果,期望自動研磨系統也能達成類似之結果,因此本文提出一種鑄件表面研磨品質回饋技術來模擬傳統老師傅邊磨邊檢的製程,期許能協助工廠建立一個自動化的鑄件表面研磨系統,後續將於文中介紹表面研磨品質回饋技術。
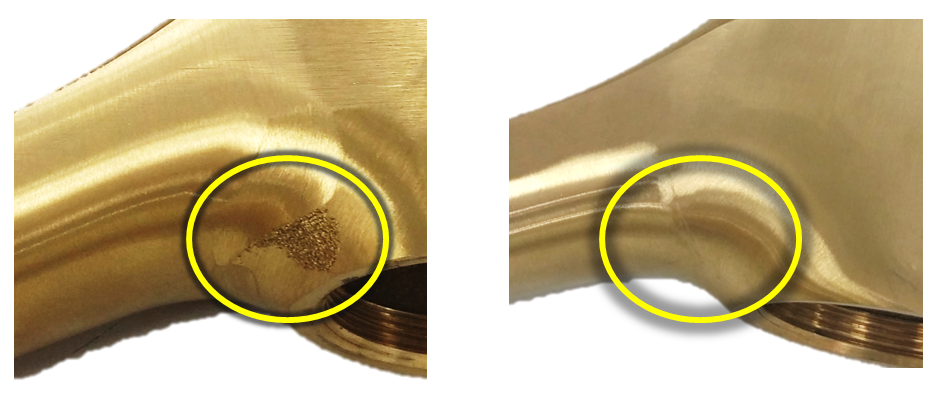
(a)傳統自動化研磨結果 (b)人工輔助研磨結果
圖1 傳統自動研磨與人工輔助研磨結果示意圖
鑄件表面研磨品質回饋技術簡介
為了解決傳統接觸式量測儀器不易檢測曲面鑄件之表面研磨程度,本文結合機器視覺與相位移輪廓法,發展3D表面研磨品質回饋技術,以達成非接觸式快速評估表面研磨情形。系統架構如圖2所示,各單元說明如下:
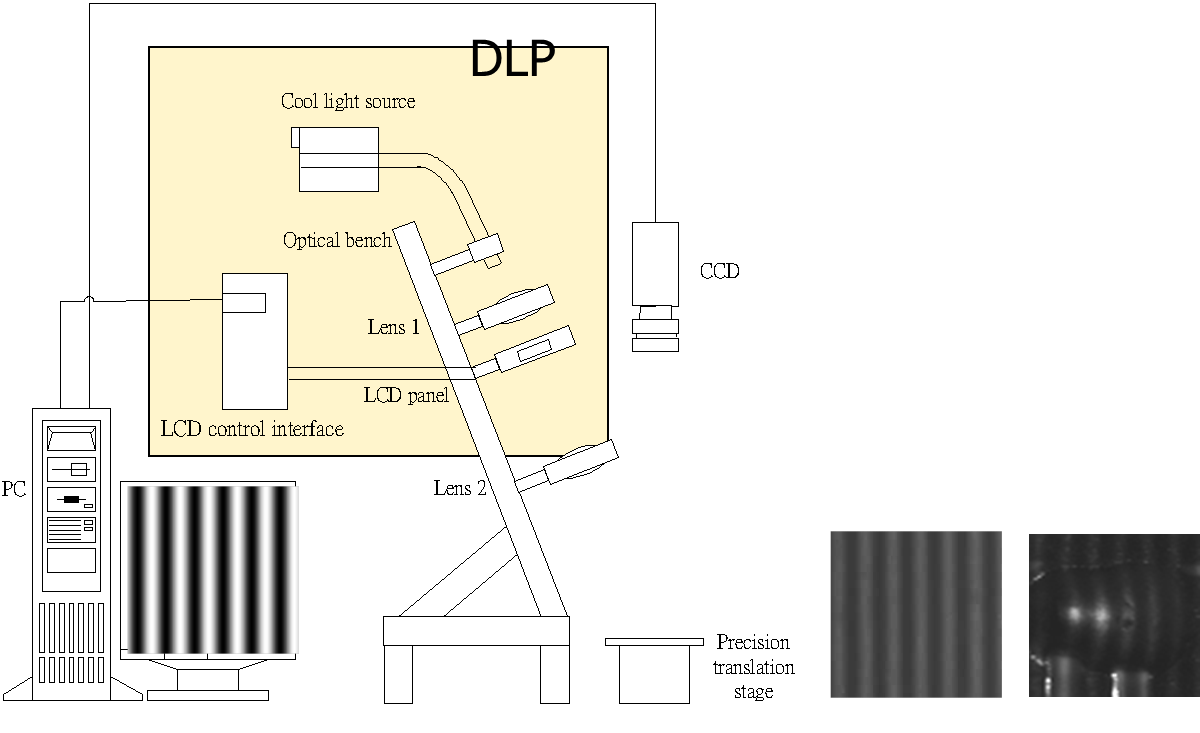
圖2 系統架構示意圖
1.多頻相位輪廓法
現有常見用於三維測距的方法包含:時差測距(Time of Flight)、三角光切法 (Triangulation)、結構光源(Structured Lighting)、立體視覺(Stereoscopic)等技術[4-8],比較多種光學三維輪廓擷取方式,整理如表1所示,相位輪廓投影是最快速且成本低,且可調整彈性高的輪廓演算法。
回文章內容列表更完整的內容歡迎訂購 2019年08月號 (單篇費用:參考材化所定價)
主推方案
無限下載/年 5000元
NT$5,000元
訂閱送出