- 回首頁
- 機械工業雜誌
- 當期雜誌
摘要:現今工業都朝向自動化與智能化發展,各家工具機廠商亦致力於提升產品的品質及自動化生產的目標,刀具磨耗的情況常常會對產品的品質、自動化生產的效率產生重大影響。本研究以機械視覺為基礎開發線上刀具磨耗檢測方法。由於端銑刀的複數刀刃與螺旋形刀具形狀不同於一般車刀,加上金屬的反光的效應,增加的端銑刀在影像拍攝困難,本研究利用刀具影像疊圖技術將立體的端銑刀展開成平面圖面,並使用影像處理的方法對展開後的刀具圖片進行磨耗檢測。實際以工具機機台進行切削加工,定時進行刀具影像疊圖並檢測刀具磨耗狀態。機械視覺系統被驗證可實際應用於刀具磨耗檢測。
Abstract:In today’s time, industries are moving toward intensive automated intelligent systems. Various machine tool manufacturers have devoted to improve quality of products to reach the goal of automated production. Tool wear has significant impact on quality of products during automated production. This research is focused on development of an online tool wear inspection method based on machine vision technology. Since the number of blades and the geometric shape of the end mills are different from turning tool, affected by add-in metallic surface reflection effects, the image of end mills are more difficult to capture. This study developed a method using tool image overlap stitch on to expand the three-dimensional end mill into a plane view. Using the image processing method, we can perform wear detection on the overlapping stitched tool image. A practical system with regular tool wear monitoring functions was developed and deployed for an actual milling process; the feasibility of the automatic online inspection system of end mill has been verified.
關鍵詞:刀具磨耗、刀具狀態監控、機械視覺、數位影像處理
Keywords:Tool wear, Tool condition monitoring, Machine vision, Digital image processing
前言
在工業4.0與物聯網的趨勢下,各項關於機台監控與智能化技術陸續推陳出新,像是在EMO 2017與JIMTOF 2018等各大工具機展覽會場上,各家廠商陸續推出溫度補償技術、軸承健康監測系統等。然而對於加工製造業者而言,加工刀具的狀態監測(Tool Condition Monitoring, TCM)至關重要,刀具不只影響加工的品質與自動化生產的效率,甚至刀具的成本幾乎佔了40%以上。由於刀具種類眾多,如刀刃形狀改變、刀刃數不同等,其中端銑刀又是立體螺旋狀刀刃,增加檢測的難度,無法有效的判定刀具的更換時機,因此如何進行刀具檢測與管理,定時監控刀具磨耗的狀況是的重要課題,本文提出一個新的想法,運用刀具影像疊圖技術,對端銑刀刀具影像進行圖片展開,希望藉此技術發出一套與工具機整合之刀具磨耗量測系統,將螺旋型的立體複數刀刃展開成直線刀表現在影像中,再以影像處理的方法檢測刀具影像疊圖後的圖片,判斷刀具磨耗量,以達到線上監控刀具磨耗狀況,判斷換刀時機。
刀具磨耗定義
目前國際上針對刀具磨耗所訂定的標準規範文件為 ISO 8688-2 :1989[1],文件中所制定的刀具磨耗類別與刀具壽命檢測標準,如圖1(a)~(e)所示刀具磨耗的現象可以分為:刀腹磨耗(flank wear)、刀面磨耗(face wear)、 凹陷磨耗(crater wear)、崩裂(chipping)、剝落(flaking)、破裂(cracks)以及災難性故障(catastrophic failure)。
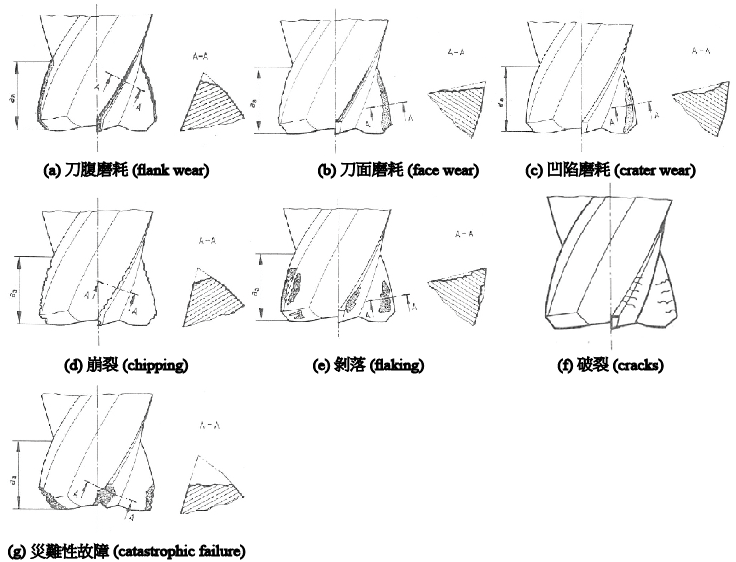
圖1 刀具磨耗種類[1]
刀具壽命標準可以定義為特定刀具磨耗類型的達到預定數值,刀腹磨耗(flank wear) 的寬度(VB)是最常用的標準。若達到所有刀刃平均0.3 mm(均勻磨耗)或任一刀刃最大0.5 mm (局部磨耗),則可認定刀具達到壽命的終點,需要進行換刀。刀腹磨耗(flank wear) 定義為在切削過程中從刀腹磨耗的材料造成的磨耗範圍。刀腹磨耗(flank wear)的情況又可分為三類,如圖2所示(a)~(c)分別為:1.均勻刀腹的磨耗(uniform flank wear):在刀腹通常呈現穩定的寬度的磨耗。2.不均勻的刀腹磨耗(non-uniform flank wear):在刀腹一些不規則的寬度的磨耗。3.局部的刀腹磨耗(localized flank wear):在刀腹特定位置所產生誇張的磨耗。
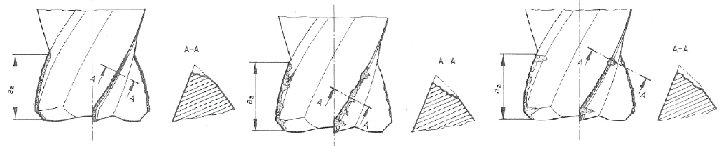
圖2 刀腹磨耗種類 [1]
更完整的內容歡迎訂購 2019年03月號 (單篇費用:參考材化所定價)